
Featured image for how does a led christmas chasing light string work
Image source: i.pinimg.com
LED Christmas chasing light strings use a controller to rapidly power individual bulbs in sequence, creating the illusion of movement. This dynamic effect is achieved through integrated circuits that regulate timing and voltage, producing popular patterns like waves, cascades, or comets. Unlike traditional incandescent sets, these energy-efficient LEDs stay cool and offer programmable, eye-catching displays perfect for festive decor.
Key Takeaways
- LEDs pulse sequentially to create the chasing effect via timed circuits.
- Microcontrollers program patterns for customizable light sequences and speeds.
- Low-voltage power ensures safety and energy efficiency during operation.
- Replaceable bulbs simplify maintenance if individual LEDs fail over time.
- Weather-resistant coatings protect lights for indoor and outdoor use.
- Timer functions automate on/off cycles to save energy effortlessly.
📑 Table of Contents
- How Does a LED Christmas Chasing Light String Work Revealed
- The Core Technology: How LEDs and Circuits Create the Chasing Effect
- Addressable LEDs: The Secret to Dynamic, Customizable Effects
- Power and Energy Efficiency: Why LED Chasing Lights Shine
- Control Systems: From Simple Switches to Smart Home Integration
- Installation, Troubleshooting, and Safety Tips
- Conclusion: The Future of Festive Lighting
How Does a LED Christmas Chasing Light String Work Revealed
The magic of Christmas lights transforms homes into winter wonderlands, with LED Christmas chasing light strings adding a dynamic, animated flair to holiday decor. Unlike traditional static lights, these strings create a mesmerizing “chasing” effect—where lights appear to move in waves, sparkles, or sequential patterns. But how do they achieve this captivating illusion? The answer lies in a blend of advanced LED technology, clever circuitry, and programmable control systems. Whether you’re wrapping your roofline, framing your windows, or crafting a festive display, understanding how these lights work can help you make informed choices and troubleshoot any issues.
In this deep dive, we’ll unravel the inner workings of LED chasing light strings. From the science behind the LEDs themselves to the controllers that orchestrate the patterns, you’ll discover why these lights are energy-efficient, long-lasting, and endlessly customizable. Whether you’re a DIY decorator, a tech enthusiast, or simply curious about how your holiday lights “dance,” this guide will illuminate every component. Let’s explore the technology, design, and practical applications that make LED chasing lights a staple of modern holiday cheer.
The Core Technology: How LEDs and Circuits Create the Chasing Effect
LEDs vs. Incandescent: The Energy-Efficient Foundation
At the heart of every LED Christmas chasing light string are Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)—semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. Unlike incandescent bulbs, which rely on heated filaments, LEDs produce light through electroluminescence, a process that generates minimal heat and consumes up to 80% less energy. This efficiency is critical for chasing lights, which often have dozens (or hundreds) of bulbs operating simultaneously.
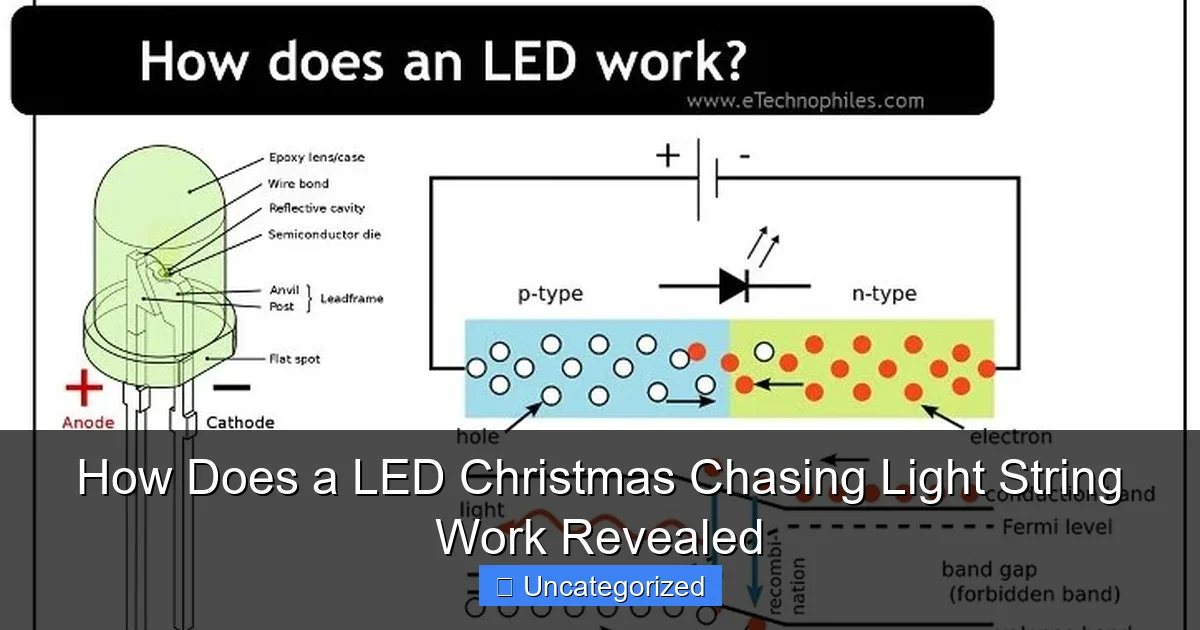
Visual guide about how does a led christmas chasing light string work
Image source: i.pinimg.com
For example, a 100-bulb LED chasing string might use only 5–10 watts of power, while an incandescent equivalent could draw 40–60 watts. This energy savings translates to lower electricity bills and reduced risk of circuit overloads. Additionally, LEDs have a lifespan of 25,000–50,000 hours—far outpacing incandescent bulbs (1,000–2,000 hours)—making them ideal for seasonal use.
Circuit Design: Series, Parallel, and Hybrid Configurations
The chasing effect is achieved through the arrangement of LEDs in the circuit. Most strings use one of three configurations:
- Series circuits: LEDs are connected end-to-end. If one bulb fails, the entire string may go out (though modern designs often include “shunt resistors” to bypass faulty LEDs).
- Parallel circuits: LEDs are connected across a shared power line. A single bulb failure won’t affect others, but this setup requires more wiring.
- Hybrid (series-parallel): A mix of both, common in chasing lights. For instance, a string might have 10 groups of 10 LEDs in series, with each group connected in parallel. This balances reliability and efficiency.
Chasing lights often use hybrid circuits to enable “zones” of LEDs. By dividing the string into segments (e.g., 10 LEDs per zone), the controller can illuminate specific zones in sequence, creating the chasing illusion.
Microcontrollers: The Brains Behind the Patterns
The “chasing” behavior is orchestrated by a microcontroller—a tiny computer embedded in the light string’s plug or control box. This chip runs pre-programmed firmware that dictates the sequence, speed, and pattern of the LEDs. For example:
- Wave pattern: Zones light up in a ripple effect (e.g., Zone 1 → Zone 2 → Zone 3).
- Comet pattern: A trailing “tail” of LEDs follows a leading light.
- Random sparkle: LEDs flicker unpredictably, mimicking fireflies.
Advanced models use Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) or Bluetooth/Wi-Fi-enabled chips, allowing users to customize patterns via smartphone apps. For instance, the Twinkly Smart LED String uses addressable LEDs (see below) and an app to sync lights with music or create custom animations.
Addressable LEDs: The Secret to Dynamic, Customizable Effects
What Are Addressable LEDs?
Traditional chasing lights use “dumb” LEDs—each bulb behaves identically, and patterns are hardwired into the controller. In contrast, addressable LEDs (e.g., WS2811, SK6812) have individual microcontrollers embedded in each bulb. This allows the main controller to send unique commands to every LED, enabling:

Visual guide about how does a led christmas chasing light string work
Image source: merrygoround.sg
- Per-bulb color control (RGB LEDs)
- Custom animations (e.g., a “twinkling star” effect)
- Synchronization with music or voice commands
For example, a 50-bulb addressable string can display a gradient of colors, with each LED transitioning smoothly from red to green to blue. This precision is impossible with non-addressable LEDs.
How Addressable LEDs Work: Data Protocols
Addressable LEDs communicate via specialized data protocols, such as:
- One-Wire Protocol (e.g., WS2812B): A single data line sends signals to all LEDs. The first LED reads its command, then forwards the rest to the next bulb.
- Clock + Data Lines (e.g., APA102): Two wires (clock and data) allow faster, more reliable communication.
These protocols rely on precise timing. For instance, a “0” bit might be a 0.35 µs pulse, while a “1” bit is 0.8 µs. The microcontroller generates these pulses at speeds up to 800 kHz, ensuring smooth animations.
Practical Example: Creating a “Candy Cane” Pattern
Imagine a 100-bulb string with addressable RGB LEDs. To create a candy cane effect:
- The controller sends a command: “Set LEDs 1–10 to red, 11–20 to white, 21–30 to red…”
- Each LED receives its color code and updates instantly.
- For animation, the controller shifts the red/white pattern down the string every 0.5 seconds, creating a “chasing” stripe.
This level of control is why addressable LEDs are popular in professional holiday displays and smart home systems.
Power and Energy Efficiency: Why LED Chasing Lights Shine
Voltage and Current Requirements
LED chasing lights operate at low voltages (typically 12V or 24V DC) to ensure safety and efficiency. The power supply (often a transformer in the plug) converts 120V AC from your wall outlet to the required DC voltage. Key specifications include:
- Wattage: A 100-bulb string might use 5–15 watts, depending on LED density and brightness.
- Amperage (Current): Measured in milliamps (mA). For example, a 12V, 10W string draws ~830 mA.
- Power Factor: High-quality supplies have a power factor >0.9, meaning they use nearly all the energy drawn.
Always check the manufacturer’s specifications to avoid overloading circuits. For large displays, use a power distribution hub to split the load across multiple outlets.
Energy Savings: A Real-World Comparison
Let’s compare a 100-bulb LED chasing string to a traditional incandescent string:
| Feature | LED Chasing String | Incandescent String |
|---|---|---|
| Power Consumption | 10 watts | 40 watts |
| Annual Cost (6 hrs/day, $0.12/kWh) | $2.63 | $10.51 |
| Lifespan | 25,000 hours | 1,200 hours |
| Heat Output | Low (touch-safe) | High (can melt plastic) |
Over a 10-year period, the LED string saves ~$78 in electricity and eliminates 19 bulb replacements. Plus, its low heat output reduces fire risk—a critical advantage for indoor/outdoor use.
Tips for Maximizing Efficiency
- Use timers: Automate lights to turn off after 6–8 hours.
- Choose “cool” white LEDs: They consume slightly less power than warm white.
- Opt for solar-powered strings: Ideal for outdoor displays with sunlight access.
Control Systems: From Simple Switches to Smart Home Integration
Basic Controllers: Preset Patterns and Manual Adjustments
Most LED chasing strings come with a basic controller—a small box with buttons to cycle through patterns (e.g., “chase,” “flash,” “steady”). These controllers use simple microcontrollers with limited memory, offering 8–12 preset modes. For example, the GE StayBright Chasing Lights include:
- Wave, Comet, Twinkle, and Steady modes
- Speed adjustment (slow, medium, fast)
- On/off timer (4, 6, or 8 hours)
To use: Plug in the lights, press the mode button until you find a pattern, and set the timer. No programming required!
Smart Controllers: Apps, Voice, and Automation
For advanced users, smart controllers unlock endless customization. These systems connect via:
- Bluetooth: Control lights from a smartphone (e.g., Twinkly).
- Wi-Fi: Integrate with smart home platforms (e.g., Philips Hue).
- RF (Radio Frequency): Use a remote control from 30+ feet away.
Smart features include:
- Color mixing: Create custom hues (e.g., “Christmas gold” or “winter blue”).
- Music sync: Lights pulse to your favorite holiday playlist.
- Geofencing: Automatically turn on when you arrive home.
- Scenes: Save and recall patterns (e.g., “Santa’s Workshop” or “Frosty’s Snowfall”).
Practical Example: Syncing Lights with a Smart Home
Imagine a Philips Hue setup:
- Install Hue addressable LED strips on your roofline.
- Use the Hue app to create a “Chasing Candy Cane” scene.
- Sync the lights to a Spotify playlist of Christmas music.
- Set a rule: “When motion is detected at the front door, activate the scene.”
Now, your lights “dance” to “Jingle Bells” when guests arrive—automatically!
Installation, Troubleshooting, and Safety Tips
Installation Best Practices
Proper installation ensures safety and longevity. Follow these tips:
- Check voltage ratings: Ensure your string matches your power supply (e.g., 120V for U.S. outlets).
- Use outdoor-rated strings for exterior displays. Look for an IP44 or higher waterproof rating.
- Secure with clips or hooks: Avoid nails, which can damage wires.
- Test before hanging: Plug in the string to verify all bulbs work and patterns function.
- Plan for expansion: Use “end-to-end” connectors to link multiple strings (e.g., for rooflines).
Common Issues and Fixes
Even the best lights can malfunction. Here’s how to troubleshoot:
- Entire string is dark: Check the fuse (often in the plug), test the outlet, or replace the power supply.
- Partial string is out: Inspect for loose bulbs or damaged wires. In series circuits, one faulty LED can kill a segment.
- Pattern is stuck: Reset the controller by unplugging for 30 seconds.
- Flickering or erratic behavior: Ensure the string isn’t overloaded (e.g., too many connected). Use a power distribution hub.
Safety First: Preventing Hazards
- Never use damaged strings: Exposed wires can cause shocks or fires.
- Use GFCI outlets outdoors: Protects against moisture-related shorts.
- Don’t daisy-chain >3 strings: Overloading can melt connectors.
- Store properly off-season: Coil loosely and avoid extreme temperatures.
Conclusion: The Future of Festive Lighting
LED Christmas chasing light strings represent a perfect fusion of art and technology. By combining energy-efficient LEDs, intelligent circuitry, and programmable control, these lights transform static decor into dynamic displays. Whether you prefer the simplicity of preset patterns or the creativity of smart home integration, understanding how they work empowers you to choose, install, and troubleshoot with confidence.
As technology advances, expect even more innovations: solar-powered addressable LEDs, AI-generated animations, and seamless integration with augmented reality (AR) apps. But one thing remains timeless—the joy of seeing your home “come alive” with the magic of light. So this holiday season, embrace the chase. Let your lights sparkle, dance, and tell a story that’s uniquely yours. After all, the best decorations aren’t just seen—they’re felt.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a LED Christmas chasing light string create its twinkling effect?
LED Christmas chasing light strings use a controller to sequence power to individual LEDs or groups, creating a “chasing” or twinkling pattern. The rapid on/off cycling mimics motion, giving the illusion of lights moving along the strand.
What makes LED chasing lights more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent ones?
LEDs consume up to 80% less energy than incandescent bulbs and generate minimal heat. Their low-voltage operation and longer lifespan make them ideal for festive displays.
Can I adjust the chasing speed or pattern on my LED Christmas lights?
Many LED chasing light strings include a controller with multiple settings (e.g., fast/slow chase, steady-on, or flashing modes). Check your product’s manual for customizable options.
Are LED chasing lights safe for outdoor use?
Yes, most LED Christmas chasing light strings are rated for outdoor use with weather-resistant coatings and waterproof connectors. Always verify the product’s IP rating before installation.
How long do LED chasing light strings typically last?
High-quality LED chasing lights can last 25,000–50,000 hours, far longer than incandescent bulbs. Their durability reduces the need for frequent replacements.
Do LED chasing lights require special maintenance?
LED Christmas chasing lights need minimal upkeep—just occasional dusting and checking for loose connections. Their sturdy design makes them less prone to damage than older lighting types.

